Untreated sleep apnea, a seemingly innocuous sleep disorder, can pose substantial long-term health risks beyond restless nights and daytime fatigue. With the prevalence of sleep apnea rising, it becomes crucial to delve into the profound impact this condition can have on overall well-being.
In this article, we at CPAPwater will explore the long-term health risks associated with untreated sleep apnea, unmasking the hidden perils beneath its seemingly harmless facade. From the intricacies of its mechanics to its potential ramifications on cardiovascular health, metabolic function, respiratory well-being, cognitive decline, and mental health, this article will uncover the multifaceted nature of untreated sleep apnea and its implications for a fulfilling life.
The Mechanics of Sleep Apnea
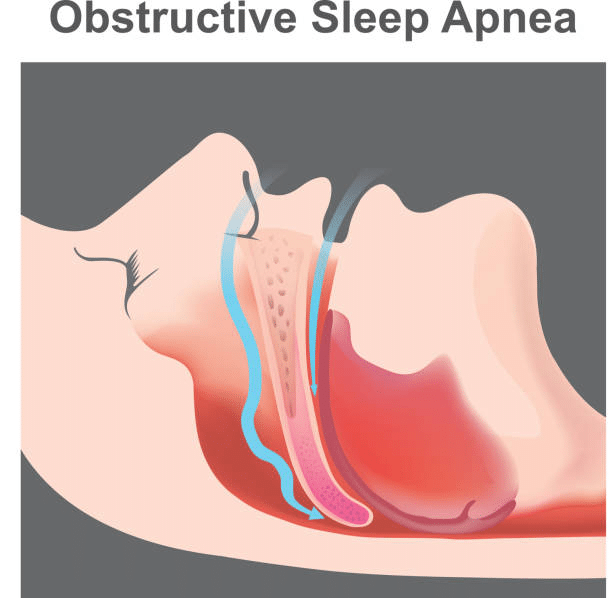
Sleep apnea encompasses different types characterized by distinct mechanisms and contributing factors. Understanding these mechanics is essential in comprehending the complexities of the condition and its potential health risks.
Types of Sleep Apnea
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): This is the most common form of sleep apnea. It occurs when the throat muscles intermittently relax and block the airway during sleep. The obstruction can lead to pauses in breathing, often accompanied by loud snoring and gasping for air as the body tries to overcome the blockage.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): Unlike OSA, central sleep apnea involves a malfunction in the central nervous system. The brain fails to signal appropriately to the muscles responsible for controlling breathing. Consequently, sleep apnea patients with CSA experience episodes of interrupted or shallow breathing during sleep without any physical obstruction in the airway.
- Mixed Sleep Apnea: Mixed sleep apnea is a combination of both obstructive and central sleep apnea. It involves a variety of airway blockages and irregular breathing patterns due to central nervous system issues.
Underlying Causes
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): The primary cause of OSA is the relaxation of throat muscles during sleep, which narrows or closes the airway. Risk factors contributing to this include excess weight or obesity, large tonsils or adenoids, structural abnormalities in the airway, and nasal congestion.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): CSA is often associated with certain medical conditions that affect the brain stem, such as congestive heart failure, stroke, brain tumors, or neurological disorders. Medications and high altitudes can also trigger or worsen central sleep apnea.
Common Symptoms And Signs of Sleep Apnea
- Excessive Daytime Sleepiness: Sleeping excessively during the day, even after a full night’s sleep, is a common symptom of sleep apnea. Individuals may struggle to stay awake, have difficulty concentrating, or experience decreased energy levels.
- Loud and Chronic Snoring: Loud, disruptive snoring is a hallmark of sleep apnea, particularly obstructive sleep apnea. The snoring may be interrupted by periods of silence when breathing stops or becomes shallow.
- Pauses in Breathing: Witnessed episodes of breathing cessation during sleep are a significant red flag for sleep apnea. These pauses can last for several seconds and may be followed by gasping or choking sensations as the body tries to resume normal breathing.
- Fragmented Sleep and Insomnia: Sleep apnea often leads to restless, fragmented sleep patterns. Individuals may wake up frequently throughout the night or experience difficulty to fall asleep (insomnia).
- Morning Headaches: Sleep apnea can cause morning headaches due to the drop in oxygen levels and the body’s response to interrupted breathing during sleep.
Short-Term Consequences of Untreated Sleep Apnea
Untreated sleep apnea can have immediate and noticeable effects on various aspects of an individual’s life, from sleep quality and daytime functioning to cognitive performance and mental well-being.
Impact on Sleep Quality And Daytime Functioning
- Disrupted Sleep Architecture: Sleep apnea disrupts the standard sleep architecture, preventing individuals from experiencing the restorative benefits of each sleep stage. The frequent awakenings due to breathing pauses can lead to fragmented sleep, reducing sleep efficiency and poor sleep quality.
- Excessive Daytime Sleepiness: The constant sleep disruptions caused by undiagnosed sleep apnea can leave individuals feeling excessively sleepy and fatigued during the day. This excessive daytime sleepiness can impair concentration, memory, and the ability to perform daily tasks effectively.
- Morning Headaches and Dry Mouth: Untreated sleep apnea often leads to morning headaches and dry mouth due to intermittent oxygen deprivation and increased effort to breathe during sleep.
Increased Risk of Accidents And Decreased Cognitive Performance
- Impaired Alertness and Attention: Sleep apnea compromises cognitive function, affecting attention, concentration, and alertness. This impairment can impact productivity, increase the risk of errors, and hinder performance in various tasks, including work-related activities, driving, and operating machinery.
- Higher Risk of Accidents: The combination of excessive daytime sleepiness, impaired attention, and decreased alertness can significantly increase the risk of accidents, both on the road and in occupational settings. Untreated sleep apnea increases the likelihood of individuals being involved in motor vehicle accidents or experiencing workplace-related incidents.
- Decreased Cognitive Performance: Studies have shown that untreated sleep apnea is associated with reduced cognitive abilities, including difficulties with memory, learning, problem-solving, and executive functions. These cognitive impairments can impact academic and professional performance and hinder overall cognitive development.
Relationship Between Sleep Apnea And Mood Disorders
- Depression: Untreated sleep apnea has been linked to an increased risk of depression. Chronic sleep disruptions and oxygen deprivation can disrupt neurotransmitter balance and contribute to changes in mood regulation, potentially leading to the development or exacerbation of depressive symptoms.
- Anxiety: Sleep apnea is also associated with an increased likelihood of experiencing anxiety symptoms. The constant fatigue, uncertainty, and disrupted sleep patterns can heighten feelings of restlessness, worry, and nervousness.
- Irritability and Emotional Instability: Sleep apnea can contribute to irritability, mood swings, and emotional instability. The impact of fragmented sleep, daytime sleepiness, and the overall strain on mental well-being can lead to heightened emotional reactivity and a decreased tolerance for stressors.
Understanding the short-term consequences of untreated sleep apnea sheds light on the urgency of seeking proper diagnosis and treatment.
Long-Term Health Risks Associated With Untreated Sleep Apnea
Untreated sleep apnea can have significant long-term consequences, affecting various aspects of health and well-being. Understanding these risks highlights the importance of timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment.
Cardiovascular Complications
- High Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Disease: Sleep apnea is closely associated with high blood pressure (hypertension). The repeated episodes of breathing pauses and oxygen deprivation during sleep can lead to increased blood pressure levels, putting additional strain on the heart and increasing the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
- Increased Risk of Heart Attack and Stroke: Individuals with untreated sleep apnea have a higher risk of heart attacks and strokes. The oxygen desaturation and fluctuation caused by interrupted breathing can trigger inflammation, blood clot formation, and damage to blood vessels, further predisposing them to cardiovascular events.
- Relationship between Sleep Apnea and Arrhythmias: Sleep apnea has been linked to developing arrhythmias and irregular heart rhythms. The disruptions in breathing patterns and the resulting fluctuation in oxygen levels can cause electrical instability in the heart, increasing the likelihood of experiencing abnormal heart rhythms such as atrial fibrillation.
Metabolic and Endocrine Disorders
- Type 2 Diabetes and Insulin Resistance: Untreated sleep apnea increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The sleep disruptions and oxidative stress caused by sleep apnea can impair insulin sensitivity, leading to insulin resistance and reduced glucose regulation.
- Hormonal Imbalances and Weight Gain: Sleep apnea disrupts the balance of hormones in appetite regulation. Individuals with untreated sleep apnea often experience hormonal imbalances, including elevated levels of ghrelin (the hunger hormone) and decreased levels of leptin (the satiety hormone). These imbalances contribute to increased food cravings, overeating, and weight gain.
- Impact of Sleep Apnea on Leptin and Ghrelin Levels: Sleep apnea can lead to dysregulation of leptin and ghrelin levels, exacerbating the risk of obesity and metabolic dysfunction. Leptin resistance and elevated ghrelin levels can disrupt the body’s ability to regulate energy balance and contribute to the development of obesity.
Also Read: The Connection Between Sleep Apnea and Type 2 Diabetes
Respiratory Issues And Lung Disorders
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Untreated sleep apnea can contribute to developing or worsening chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The intermittent drops in oxygen levels and the strain on the respiratory system can lead to inflammation, airway remodeling, and increased susceptibility to COPD.
- Asthma Exacerbation and Increased Respiratory Infections: Sleep apnea can trigger asthma attacks and worsen respiratory conditions. The fragmented sleep, airway obstruction, and oxygen desaturation can increase airway inflammation and hypersensitivity, leading to more frequent asthma exacerbations. Moreover, untreated sleep apnea weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to respiratory infections.
- Sleep Apnea’s Effect on Lung Function and Oxygen Levels: The repetitive pauses in breathing during sleep deprive the body of oxygen and disrupt the regular oxygen-carbon dioxide exchange. Over time, this can impair lung function, decrease oxygen saturation levels, and contribute to respiratory complications.
Cognitive Decline And Neurological Disorders
- Memory Problems and Cognitive Impairment: The repeated disruptions in sleep architecture and decreased oxygen supply to the brain can affect memory consolidation, learning, and information processing. Individuals with untreated sleep apnea may experience difficulties with attention, concentration, executive function, and overall cognitive performance.
- Increased Risk of Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease: Growing evidence suggests a link between untreated sleep apnea and an increased risk of developing dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Chronic oxygen deprivation and disrupted sleep patterns may contribute to the accumulation of amyloid plaques in the brain, characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Sleep Apnea’s Impact on Brain Structure and Function: Sleep apnea can lead to structural and functional changes in the brain. Imaging studies have revealed alterations in the gray matter, particularly in areas involved in memory, executive function, and emotional regulation. These changes may contribute to cognitive decline and increased risk of neurological disorders associated with undiagnosed sleep apnea.
Impact of Untreated Sleep Apnea on Mental Health

Untreated sleep apnea can profoundly affect mental health, contributing to developing or exacerbating various mental health conditions. Recognizing the impact of mild sleep apnea on mental well-being is crucial in promoting comprehensive treatment and addressing these associated concerns.
Relationship between Sleep Apnea and Depression
Untreated sleep apnea has been strongly linked to an increased risk of depression. The chronic sleep disruptions, oxygen deprivation, and physiological stress caused by sleep apnea can contribute to depressive symptoms. The following factors may explain the relationship between sleep apnea and depression:
- Neurotransmitter Imbalances: Sleep apnea disrupts the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, including serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which are involved in mood regulation. The imbalances caused by sleep apnea can contribute to the onset or worsening of depressive symptoms.
- Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: The intermittent drops in oxygen levels and fragmented sleep patterns associated with sleep apnea can trigger inflammation and oxidative stress in the body. These inflammatory processes have been linked to the development of depression.
- Daytime Fatigue and Functioning: The excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue experienced by individuals with sleep apnea can significantly impact their quality of life and overall functioning. The ongoing struggle to stay awake and maintain energy levels can contribute to despair, hopelessness, and diminished interest in previously enjoyed activities.
Effects of Sleep Apnea on Anxiety And Mood Disorders
Sleep apnea can also impact anxiety levels and mood disorders. The following factors highlight the relationship between sleep apnea and these conditions:
- Sympathetic Nervous System Activation: Sleep apnea triggers the activation of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body’s stress response. The persistent physiological stress caused by sleep apnea can contribute to feelings of anxiety and heightened reactivity to stressors.
- Sleep Disruptions and Emotional Regulation: The fragmented sleep patterns associated with sleep apnea can disrupt emotional regulation processes. Due to insufficient restorative sleep, individuals may experience increased emotional reactivity, irritability, and mood swings.
- Quality of Life Impact: Sleep apnea can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life, leading to frustration, decreased social engagement, and limitations in daily activities. These factors can contribute to developing or worsening anxiety and mood disorders.
Associations Between Sleep Apnea And ADHD
Growing evidence suggests a potential association between sleep apnea and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), particularly in children. The following factors contribute to this relationship:
- Similar Symptoms and Overlapping Characteristics: Sleep apnea and ADHD share common symptoms, including daytime sleepiness, inattention, and impaired cognitive function. The overlapping features can make it challenging to distinguish between the two conditions.
- Sleep Disruptions and ADHD Symptoms: Sleep disruptions caused by sleep apnea can exacerbate symptoms of ADHD, such as inattention and hyperactivity. Sleep can further impair cognitive function and attentional control, worsening ADHD-related difficulties.
- Impact on Behavioral and Emotional Functioning: Sleep apnea can affect behavioral and emotional functioning in children with ADHD. Inadequate sleep can lead to increased impulsivity, irritability, and difficulties with emotional regulation, which can further complicate ADHD management.
Sleep Apnea’s Influence In The Quality Of Life And Well-Being
Untreated sleep apnea can significantly impact an individual’s overall quality of life and well-being. The following factors highlight the influence of sleep apnea on these aspects:
- Daytime Functioning: The excessive daytime sleepiness, fatigue, and cognitive impairments associated with untreated sleep apnea can affect an individual’s ability to function optimally during the day. Tasks such as work, studying, and social interactions may become challenging, leading to decreased productivity and satisfaction.
- Relationships and Social Well-being: Sleep apnea can affect personal relationships and social interactions. Sleep apnea symptoms, such as loud snoring and disrupted sleep, can disrupt the rest of bed partners, leading to strained relationships. Additionally, individuals with sleep apnea may avoid social activities due to embarrassment or fatigue, leading to social isolation and decreased well-being.
- Emotional Well-being: The impact of untreated sleep apnea on sleep quality and daytime functioning can contribute to emotional distress. Frustration, irritability, and mood swings may arise due to chronic sleep deprivation and impaired cognitive function. These emotional disturbances can further affect overall well-being and mental health.
- Physical Health: The systemic effects of untreated sleep apnea can affect physical health. The increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, and respiratory complications associated with sleep apnea can further diminish overall well-being and quality of life.
Recognizing the impact of untreated sleep apnea on mental health, overall quality of life, and well-being emphasizes the importance of seeking proper diagnosis and treatment.
The Importance of Diagnosis And Treatment
Diagnosing and treating obstructive sleep apnea is crucial for mitigating long-term health risks and improving overall well-being. Proper identification of sleep apnea, followed by appropriate interventions, can make a significant difference in managing the condition effectively.
Diagnostic Methods for Sleep Apnea
- Overnight Polysomnography (PSG): PSG is considered the gold standard for diagnosing sleep apnea. It involves sleeping in a sleep laboratory while various physiological parameters, including brain activity, respiratory patterns, heart rate, and oxygen levels, are monitored. This comprehensive test provides detailed information about the severity and characteristics of sleep apnea.
- Home Sleep Apnea Testing (HSAT): HSAT is an alternative diagnostic option that can be conducted in the comfort of one’s own home. It involves wearing portable monitoring devices that measure breathing patterns, oxygen levels, and other relevant parameters. HSAT is typically recommended for individuals with a high suspicion of severe obstructive sleep apnea.
Available Treatment Options
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy: CPAP therapy is the most common and effective treatment for sleep apnea. It involves wearing a mask over the nose or mouth during sleep, which delivers a continuous flow of pressurized air to keep the airway open. CPAP helps prevent breathing pauses, alleviates snoring, and promotes restful sleep by effectively treating sleep disordered breathing.
- Mandibular Advancement Devices (MADs): MADs are oral appliances that help treat sleep apnea by repositioning the lower jaw and tongue, thus opening the airway. These custom-fitted devices are worn during sleep and can be an effective alternative for individuals who find CPAP therapy uncomfortable or prefer a non-invasive treatment.
- Surgical Interventions: In some instances, doctors may recommend surgical interventions to address structural abnormalities that contribute to sleep apnea. Procedures such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) and maxillomandibular advancement (MMA) aim to remove or reposition tissues in the throat or reposition the jaws to widen the airway and improve airflow.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Sleep Apnea
- Weight Loss and Exercise: Obesity is a significant risk factor for sleep apnea. Losing weight through a combination of healthy eating and regular physical activity can help reduce the severity of sleep apnea symptoms. Weight loss can lead to a decrease in excess tissue around the neck and improve airway function.
- Sleep Position Adjustments: Sleeping on the back can worsen sleep apnea symptoms. Encouraging individuals to sleep on their sides or using positional aids such as body pillows can help keep the airway open and reduce the occurrence of breathing pauses.
- Avoidance of Alcohol and Sedatives: Alcohol and sedatives relax the muscles in the throat, increasing the likelihood of airway collapse during sleep. Avoiding or minimizing the consumption of alcohol and sedatives, incredibly close to bedtime, can help improve sleep apnea symptoms.
Doctors should individualize the diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea based on the severity of the condition and the patient’s specific needs.
Potential Complications From Untreated Sleep Apnea

The consequences of leaving sleep apnea untreated extend beyond long-term health risks. Failure to address sleep apnea can lead to various complications that affect different aspects of life, including pregnancy outcomes, safety, and social well-being.
Impact on Pregnancy Outcomes
Untreated severe sleep apnea during pregnancy can harm both the mother and the developing baby. The following complications, including increased risks of gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and other sleep disorders, are associated with untreated sleep apnea in pregnant women.
- Gestational Diabetes: Sleep apnea increases the risk of developing gestational diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Chronic sleep disruptions and intermittent drops in oxygen levels can affect glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, contributing to the development of gestational diabetes.
- Preeclampsia: An increased risk of preeclampsia, a potentially serious condition characterized by high blood pressure and organ damage during pregnancy, is also associated with sleep apnea. We do not fully understand the exact mechanisms that link sleep apnea and preeclampsia. However, researchers believe that sleep apnea’s physiological stress contributes to the development of preeclampsia.
Increased Risk of Accidents And Injuries In Various Settings
Untreated sleep apnea can significantly impair daytime functioning, increasing the risk of accidents and injuries. The following settings particularly affect:
- Workplace: Sleep apnea-related daytime sleepiness and cognitive impairments can reduce productivity, increase errors, and jeopardize workplace safety. Individuals with untreated sleep apnea may experience difficulties staying alert, concentrating, and maintaining optimal performance, increasing the risk of accidents or injuries in various work environments.
- Driving: Sleep apnea is a significant contributor to drowsy driving accidents. Excessive daytime sleepiness and decreased alertness can impair a driver’s reaction time, judgment, and decision-making abilities. Studies have shown that individuals with untreated sleep apnea have an increased risk of motor vehicle accidents, making it crucial to address the condition to ensure road safety.
Social And Relationship Implications
Untreated sleep apnea can have social and relationship implications due to the following factors:
- Snoring: Loud and disruptive snoring is a common symptom of sleep apnea. It can disturb bed partners’ sleep, leading to strained relationships and conflicts. The persistent snoring may disrupt the rest of the individual with sleep apnea and their partner, resulting in sleep deprivation.
- Sleep Disruption: Sleep apnea can cause frequent awakenings at night, leading to sleep disruption for the individual and their bed partner. Constant interruptions can affect sleep quality, causing both parties irritability, fatigue, and decreased well-being.
Addressing sleep apnea through appropriate diagnosis and treatment is crucial to mitigate these potential complications.
Confronting The Risks Of Untreated Sleep Apnea

The long-term health risks associated with untreated sleep apnea are significant and underscore the importance of seeking diagnosis and treatment. Cardiovascular complications, including high blood pressure, increased risk of heart attacks and strokes, and arrhythmias, pose a grave threat to heart health.
Endocrine and metabolic syndrome, such as type 2 diabetes and hormonal imbalances, further highlight the need to address sleep apnea to prevent the development of chronic conditions. Additionally, respiratory issues, cognitive decline, and mental health disturbances amplify the multifaceted nature of the risks involved.
To combat these risks, early intervention and comprehensive treatment approaches are essential. Raising awareness about sleep apnea and its potential health risks is vital, as it empowers individuals to prioritize their sleep health and take proactive steps toward a healthier future.
By recognizing the profound impact of untreated sleep apnea and taking appropriate action, individuals can safeguard their cardiovascular health, metabolic function, respiratory well-being, cognitive abilities, and mental well-being. Let us prioritize sleep health and promote a greater understanding of sleep apnea, ensuring a better quality of life for ourselves and those around us.
Address the long-term health risks associated with untreated sleep apnea by taking action today. Explore our range of CPAP accessories designed to support effective treatment and enhance your well-being. Visit our store to invest in your health for the future.
What are your key takeaways from this article?



